What is Leverage?
Leverage is a mechanism that lets traders control larger positions using smaller capital. By choosing to trade with leverage, market exposure increases, amplifying both potential profits and losses. Higher leverage can boost flexibility, but it also raises risk if markets move fast. Simply put, leverage allows efficiency when used responsibly, and every forex broker sets limits to protect clients. Education, discipline, and planning help traders manage exposure across market conditions.
What is leverage in trading?
Leverage in trading allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller deposit, increasing exposure to the market. When you trade with a stockbroker, leverage means you only commit a percentage of the full value of a position, while borrowing the rest. This increases total exposure to price changes in underlying assets. It is important to understand how CFDs work and whether leverage suits your risk profile. While leverage can amplify profits when market moves are favourable, losses can grow just as quickly. Used wisely, traders use leverage to improve capital efficiency.
How does leverage trading work?
Leverage trading allows you to control a larger market exposure by using a relatively small upfront deposit, called margin. When you place a leveraged trade, you only put into a trade a portion of the value of the trade, while the broker effectively finances the rest. This means you can open a position worth far more than your initial capital.
Your trade size determines your overall position size, and both directly affect the value of your position. As a result, even small market movements can have a noticeable impact, increasing potential profits and losses. This is especially true when using high leverage ratios, where traders consciously take the high risk in exchange for greater exposure.
Leverage can be applied to various instruments, including shares of a company, ETFs, or a CFD linked to a trade and the company’s share price. Ultimately, the leverage ratio shows how much exposure you gain compared to the capital you commit.
Leverage trading example
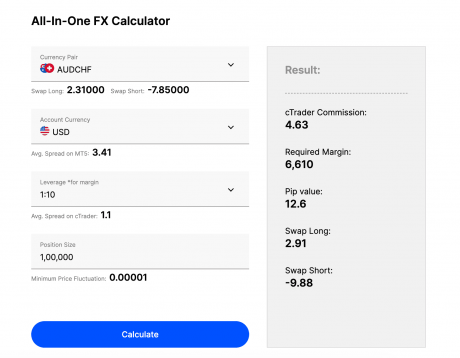
Imagine buying 1,000 shares of a company priced at $1 each. In a traditional cash deal, you’d be required to pay the full $1,000 upfront to open a trade, before fees. That’s the cost of owning the shares outright.
Leverage changes this dynamic. With trading on margin, a trader can control the same $1,000 market value by depositing only part of it. With a 10% margin requirement (or 1:10 leverage), you need just $100 to open a position, while your gains or profit or loss are calculated on the entire exposure. This means a relatively small outlay can control a larger position and deliver increased exposure to an underlying asset. For comparison, some markets may allow a deposit example of $1, depending on margin rules.
If the price rises by 50p, each share is worth $1.50 and the position totals $1,500. Closing here results in a $500 gain, far exceeding the initial margin amount of $100. The same logic is true if you went long and the market moves against you. The reverse would be true if the price drops by 50p, creating a $500 loss.
This is why leverage, whether accessed via desktop or mobile trading, amplifies outcomes in both directions.
Leverage ratios explained

Leverage ratios help traders understand how much market exposure they can control with a smaller investment. In simple terms, leverage allows you to open larger positions while committing only a fraction of this cost upfront. In forex, this means you can buy or sell currency pairs without paying the full value of the position. Compared vs unleveraged trade, potential profits and losses are magnified, making risk management essential. Successful trading depends on using leverage wisely, as even small price moves can significantly impact your amount of capital if positions are poorly managed.
Margin calls

A margin call happens when equity falls too low, and positions may be liquidated to protect the trader’s account to fall below zero. This risk increases when you’re trading with high leverage or oversized positions. Market swings, including sudden moves in a company’s share price, can quickly impact a position’s value.
Managing margin is a core responsibility for every trader. You must keep enough funds in your account to cover margin requirements and potential losses, not just the minimum needed to open trades. To stay safe, keep funds available to trade above what you’d pay in margin, so your account to cover volatility remains resilient.
What can you trade with leverage?

Here are the main markets you can access when trading with leverage:
- Foreign exchange markets
Currency pairs are the most popular choice for leveraged trading, especially in forex, where price movements are frequent but relatively tiny and liquidity is high. This market allows traders to benefit from both rising and falling exchange rates using leverage. - Contracts for Difference
With CFDs, you speculate on price movements without owning the underlying asset. This makes it possible to trade with leverage across multiple markets from a single account. - Stock market instruments
You can gain exposure to a single stock without buying shares outright. This approach is common for short-term strategies and is widely used by traders interested in trading stocks with smaller upfront capital. - Equity indices
An index tracks the performance of a group of companies, such as major national or global markets. Trading indices with margin lets you speculate on the overall direction of an economy rather than individual companies. - Commodities
Popular assets like gold, oil, or agricultural products fall under the commodity category. These markets are often influenced by global events, making them attractive for leveraged strategies. - Specialised leveraged instruments
Many brokers offer leveraged products that combine margin trading with flexible position sizing, all accessible through an online trading platform designed for fast execution and risk management. - UK-specific trading formats
In the UK, traders often use spread betting and CFDs to speculate on market movements, benefiting from margin trading while following local regulations.
Each of these markets offers different opportunities and risks, so understanding how leverage works in each case is essential before you start trading.
The benefits & risks of using leverage in trading

Leverage is one of the most powerful tools available to modern traders. When used correctly, it can significantly enhance opportunities, but it also introduces important considerations that should never be ignored. Below is a clear breakdown of the main benefits and risks.
Benefits
- Access larger positions with less capital
Leverage allows traders to control a position by committing only a fraction of the full value of that position. This means you can participate in markets that would otherwise require substantial capital, making trading more accessible without tying up all your funds. - Potential for magnified returns
Because profits are calculated on the total position size, a well-timed move can help you make a profit that would normally require a much larger investment. This is especially attractive in fast-moving markets such as forex, where small price movements can be efficiently exploited. - Efficient capital allocation
Using a leveraged trade frees up capital that can be used elsewhere. Instead of allocating all your funds to one opportunity, you can diversify across multiple instruments, strategies, or timeframes while keeping flexibility in your account. - Flexible exposure through leverage settings
The leverage ratio allows traders to adjust their exposure based on experience and risk tolerance. Whether trading a single asset or a major index, leverage provides control over position sizing without changing market access. - Opportunity in rising and falling markets
Leverage makes it possible to profit from both bullish and bearish conditions. Traders can benefit from downward price movements just as easily as upward ones, adding versatility to different market environments. - Extended trading availability
Many leveraged markets offer near-continuous trading hours. This allows traders to react to global news, economic data, or volatility without being restricted to traditional exchange schedules. - Lower barrier to execution
Leverage simplifies the process to open the trade, reducing capital requirements while still providing exposure to full market movements
Risks
- Magnified downside exposure
Just as gains increase, so do losses on unsuccessful trades. This is the core of the risks of trading with leverage, as price movements against you impact the full position size, not just your initial margin. - Margin calls and forced actions
If the market moves sharply against your position, you may need to add funds to maintain it. Failing to do so can result in automatic position closure, increasing the risk of losing your money faster than expected.
Risk-management with leverage

Risk management is essential when trading with leverage, especially in forex markets where price moves can be fast.
- First, control position size. In any leveraged trade, risk only a small percentage of your capital per position so a single loss cannot damage your account. Always calculate your initial outlay and set clear limits before entering the market.
- Second, use protective stops. Every asset can move against you, even if you went long on your trade with strong conviction. Stop-loss orders help cap downside risk and remove emotion from decision-making.
- Third, assess leverage realistically. Ask yourself whether you can afford to take the high leverage, and consider whether you understand how margin, volatility, and losses are amplified under stress.
Top 3 strategies for using leverage in trading
Leverage can enhance results when used correctly, but it requires discipline and control. Below are the top 3 strategies for using leverage wisely:
- Scale into positions carefully
Start with lower exposure and increase only after confirmation. This approach helps manage trading decisions logically, limiting emotional reactions when markets move fast. - Control risk before entering the market
Always calculate potential profit or loss in advance and use stop-loss orders. Leverage comes with a high risk of losing capital, so risk management must come first. - Trade with the trend and manage margin
If you went long and the share price shows strong momentum, controlled leverage can improve efficiency. A broker would put margin limits in place, so experienced traders keep their positions to reduce unnecessary exposure and drawdowns.
FAQs
Can beginners use leverage trading?
Yes, beginners can use leverage, but only after they learn to trade with small positions and clear rules. Starting slowly helps build confidence and limits early mistakes.
Is leverage risky in trading?
Leverage can amplify both gains and losses, which makes it inherently risky. You should only use funds you can truly afford to lose and always manage risk carefully.
What is the difference between leverage and margin?
Leverage lets you control a larger position with less capital, while margin is the deposit required to open that position. In simple terms, margin is the cost, leverage is the multiplier in trading.
How much leverage should a beginner use?
A beginner should stick to low leverage levels to reduce pressure and volatility. Choosing a broker that offers negative balance protection adds an extra layer of safety.
What is leverage in crypto trading?
In crypto, leverage allows you to increase exposure to digital assets without paying the full value upfront. Because crypto markets move fast, leverage should be used conservatively.
How to trade gold with leverage?
To trade gold with leverage, focus on liquid market hours and use strict risk controls. Gold often reacts to economic news, so timing and position size matter.






